上一篇文章《深入区块链共识(三)》中,我们以BurstCoin为例,详细介绍了工程中的PoC共识算法的实现,主要集中在Plot文件内容的生成,与出块的详细交互和计算流程。
基于deadline的出块过程中,如何解决分布式节点中的时间同步问题


The solution we propose begins with a timestamp server. A timestamp server works by taking a hash of a block of items to be timestamped and widely publishing the hash, such as in a newspaper or Usenet post.[2][3][4][5] The timestamp proves that the data must have existed at the time, obviously, in order to get into the hash. Each timestamp includes the previous timestamp in its hash, forming a chain, with each additional timestamp reinforcing the ones before it.
Each block contains a Unix time timestamp. In addition to serving as a source of variation for the block hash, they also make it more difficult for an adversary to manipulate the block chain. A timestamp is accepted as valid if it is greater than the median timestamp of previous 11 blocks, and less than the network-adjusted time + 2 hours. "Network-adjusted time" is the median of the timestamps returned by all nodes connected to you. As a result block timestamps are not exactly accurate, and they do not need to be. Block times are accurate only to within an hour or two. Whenever a node connects to another node, it gets a UTC timestamp from it, and stores its offset from node-local UTC. The network-adjusted time is then the node-local UTC plus the median offset from all connected nodes. Network time is never adjusted more than 70 minutes from local system time, however. Bitcoin uses an unsigned integer for the timestamp, so the year 2038 problem is delayed for another 68 years.
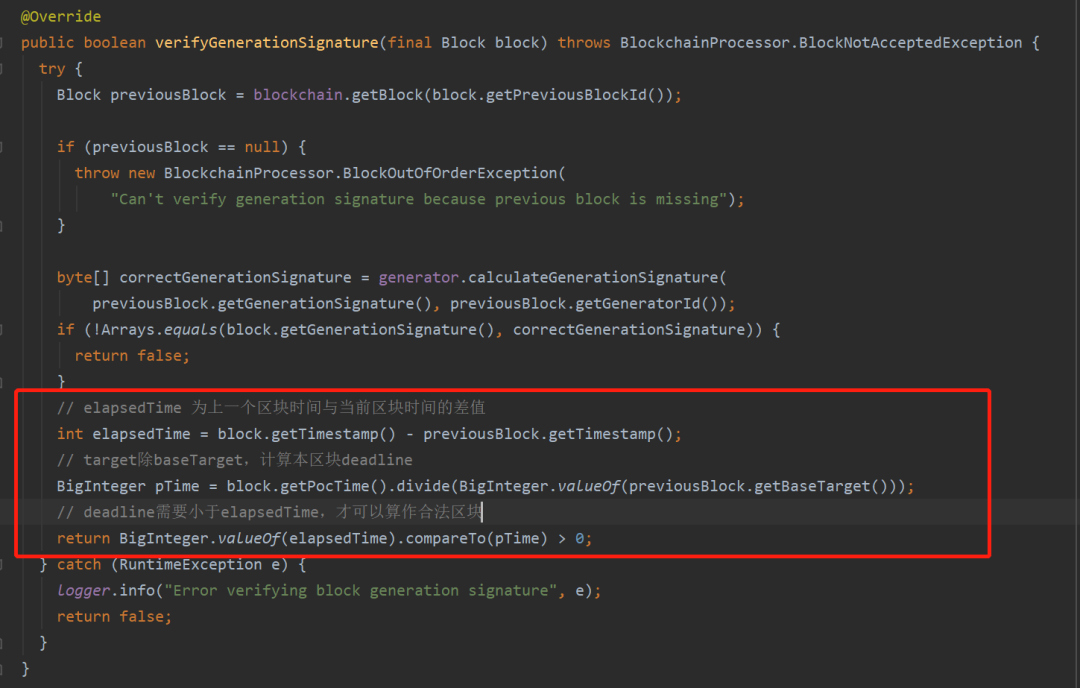
Deadline合法性的校验
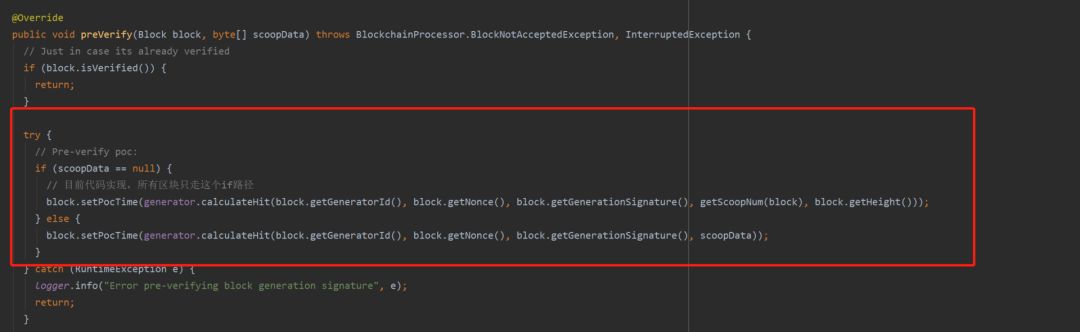
在节点收到P2P网络中的历史区块,抑或是收到矿工广播的铸造区块时,首先要对区块进行preVerify操作,此处在调用者提交的参数中,scoopData总是空值,因为在burstCoin所使用的数据存储中,block的字段没有存储scoopData。那又是如何完成验证? 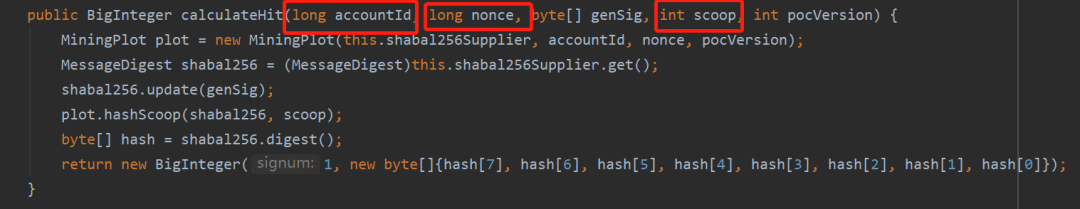
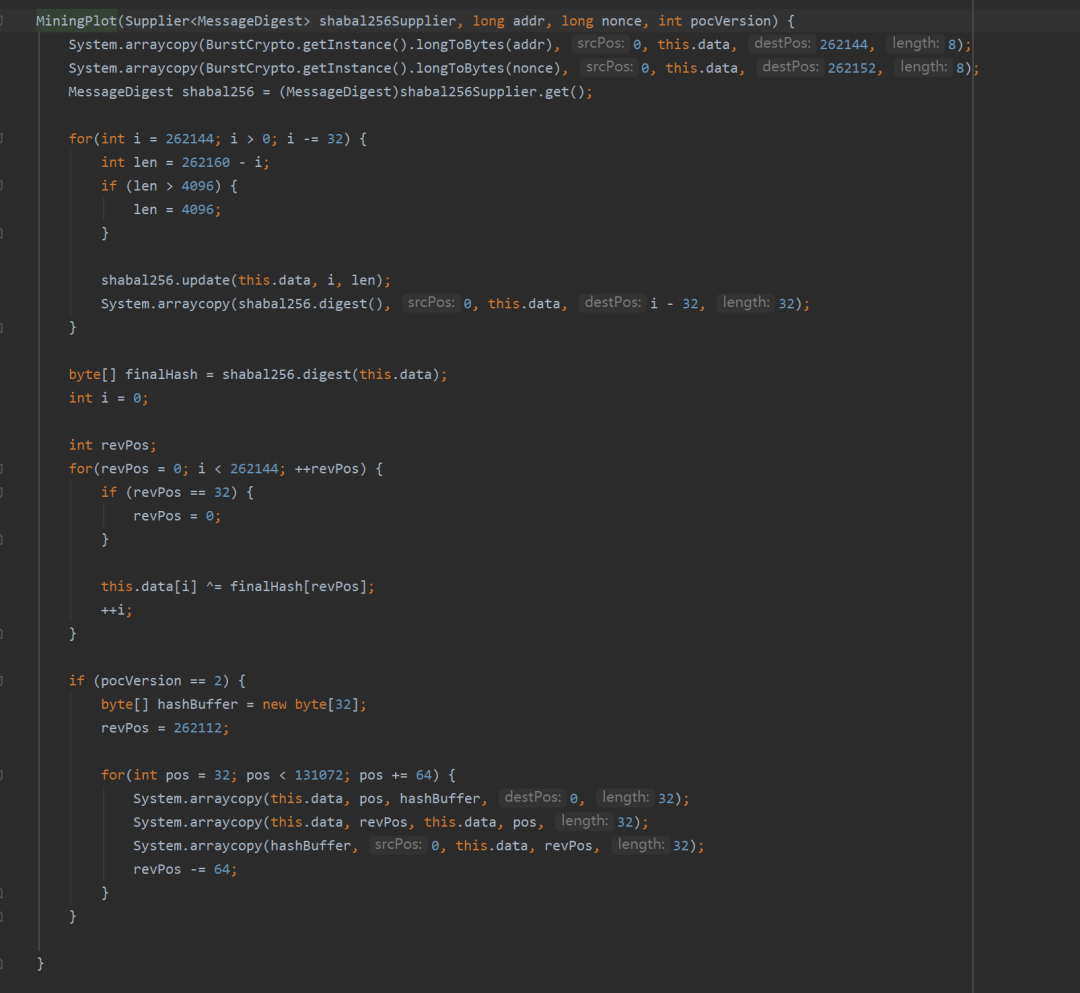
答案就在calculateHit这一方法之中,BurstCoin将其节点的一部分功能方法放到了burstKit的单独jar包中,找到其计算calculateHit方法后,我们发现,其调用了MiningPlot的初始化方法。 在MiningPlot方法中,我们可以看到,通过nonce Id,accountId两个参数,回忆Nonce文件的生成算法,我们可以得知,通过nonce Id 与 accountId,可以完全确定的生成两个Nonce文件。所以,在BurstCoin中,矿工并不需要向节点发送大小为256KB的Nonce文件,只需要在参与出块时,将区块内容与这两个参数发送给钱包节点,由钱包即可计算出整个Nonce值,同时由全网每个节点收到每个区块后都会通过计算此Nonce来计算其deadline。
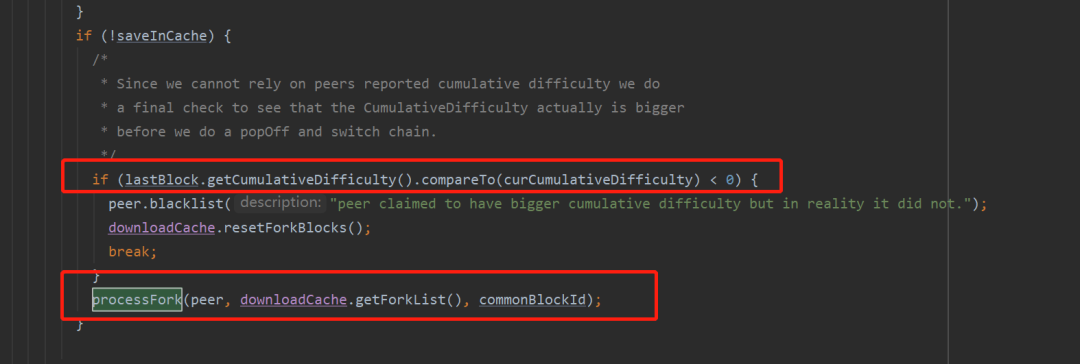
BurstCoin如何处理分叉
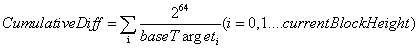

参考源
[1.]Spacemint:A Cryptocurrency Based on Proofs of Space [2.]BHD whitepaper [3.]BurstCoin Introduction Serious [4.]Proof of Space [5.]Burstcoinist [6.]Proof of Space from Stacked Expanders [7.]The Burst Dymaxion [8.]burstforum [9.]mining tutorials [10.] Cynthia DworkMoni Naor,Pricing via Processing or Combatting Junk Mail [11.] Giuseppe Ateniese, Randal C. Burns, Reza Curtmola, Joseph Herring, Lea Kissner, Zachary N. J. Peterson, and Dawn Song. Provable data possession at untrusted stores. In Peng Ning, Sabrina De Capitani di Vimercati, and Paul F. Syverson, editors, ACM CCS 07, pages 598–609. ACM Press, October 2007 [12.] Kevin D. Bowers, Ari Juels, and Alina Oprea. Proofs of retrievability: theory and implementation. In CCSW, pages 43–54, 2009 [13.] Nikolaos P. Karvelas and Aggelos Kiayias. Efficient proofs of secure erasure. In Security and Cryptography for Networks - 9th International Conference, SCN 2014, Amalfi, Italy, September 3-5, 2014. Proceedings, pages 520–537, 2014] [14.] Dziembowski, S., Faust, S., Kolmogorov, V., & Pietrzak, K. (2015). Proofs of space. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 9216(616160), 585–605. [15]Bitcoin White Paper



发表评论 取消回复